Checkout Latest News and Articles
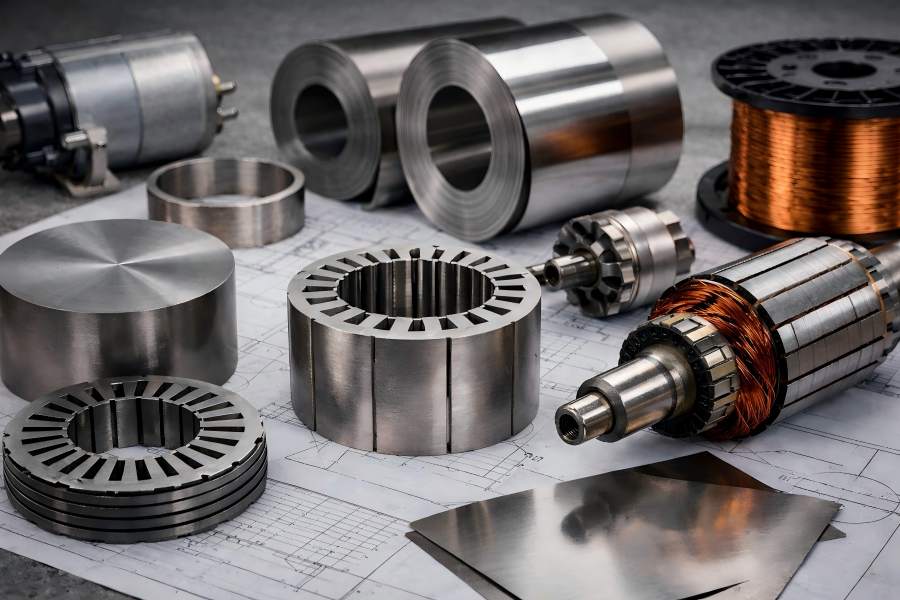
Flywheels are crucial components in energy storage systems, acting as mechanical batteries to store and release energy in industrial applications. The rotor and stator components’ designs have a significant impact on these systems’ efficiency.
Read Article
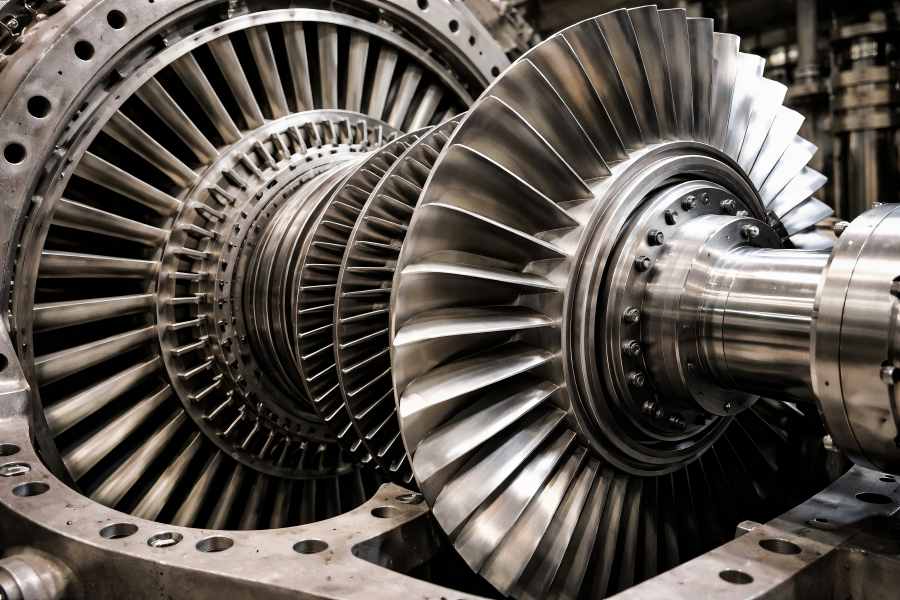
Turbines are utilized in ships, aircraft, and power plants to transform fluid energy into mechanical energy. The rotor and stator, the two primary parts, cooperate to guarantee effective operation.
Read Article
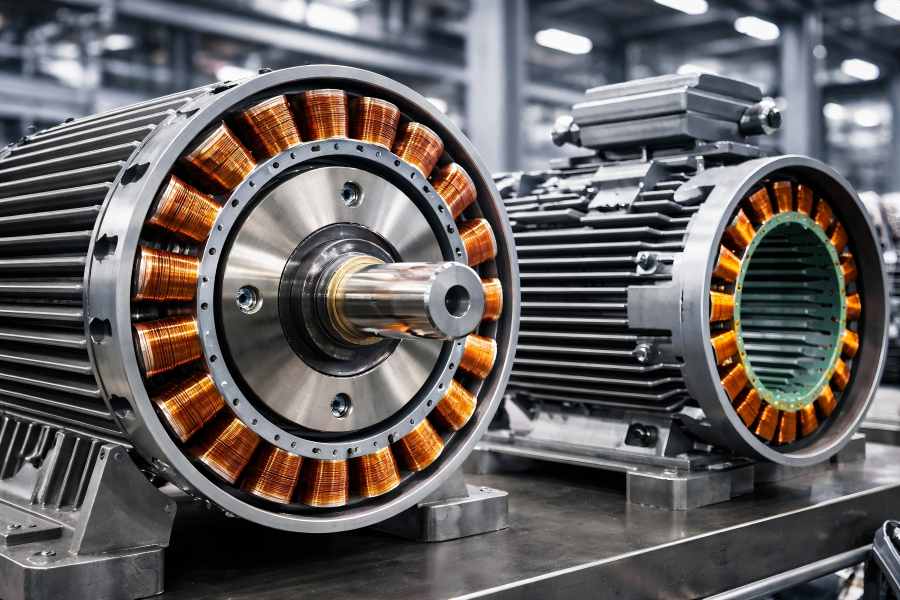
Electric motors drive machines in industries, vehicles, and appliances. The stator, rotor, slots, teeth, and back iron form the motor’s magnetic structure, impacting efficiency, torque, noise, and reliability. Understanding these components highlights the importance of design choices.
Read Article
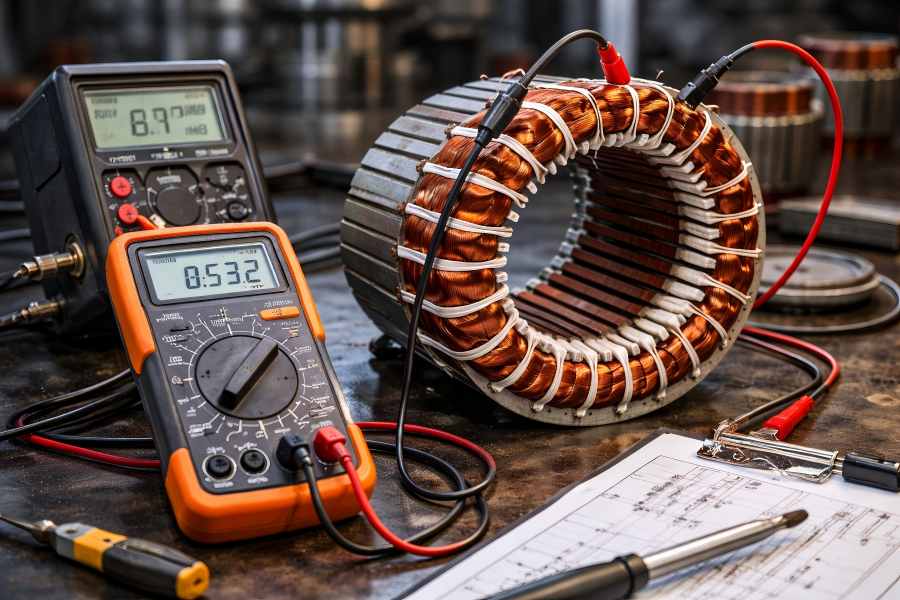
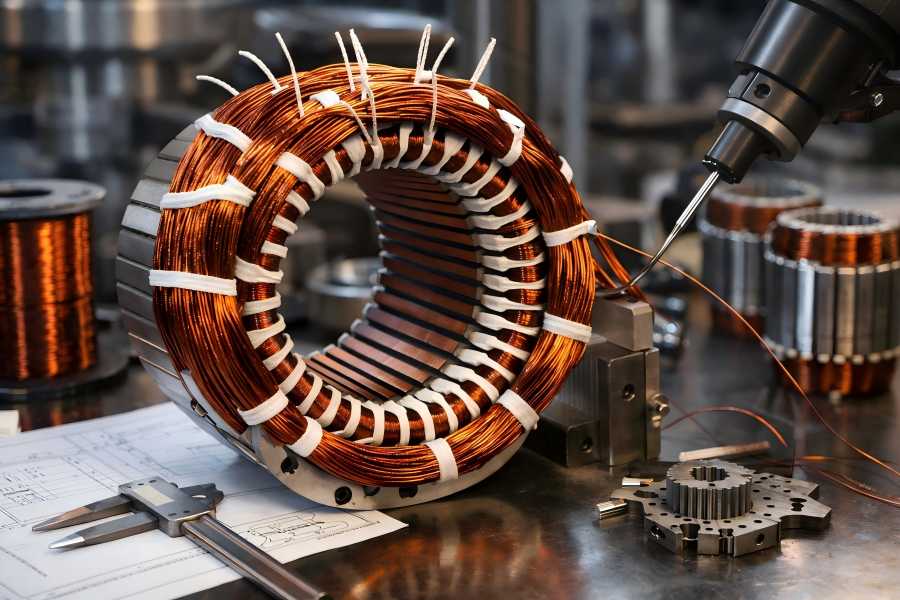
Motor windings, in both the stator and rotor, are essential for proper operation. Faulty windings can cause inefficiency, overheating, and even motor failure. Early detection is crucial for maintaining motor reliability and efficiency.
Read Article
Electric motor performance and overall efficiency are largely dependent on the stator slot fill factor. By optimizing this factor, manufacturers can improve the motor’s copper utilization, reduce losses, and enhance thermal performance. However, achieving the ideal fill factor requires careful attention to design, manufacturing processes, and material selection.
Read Article
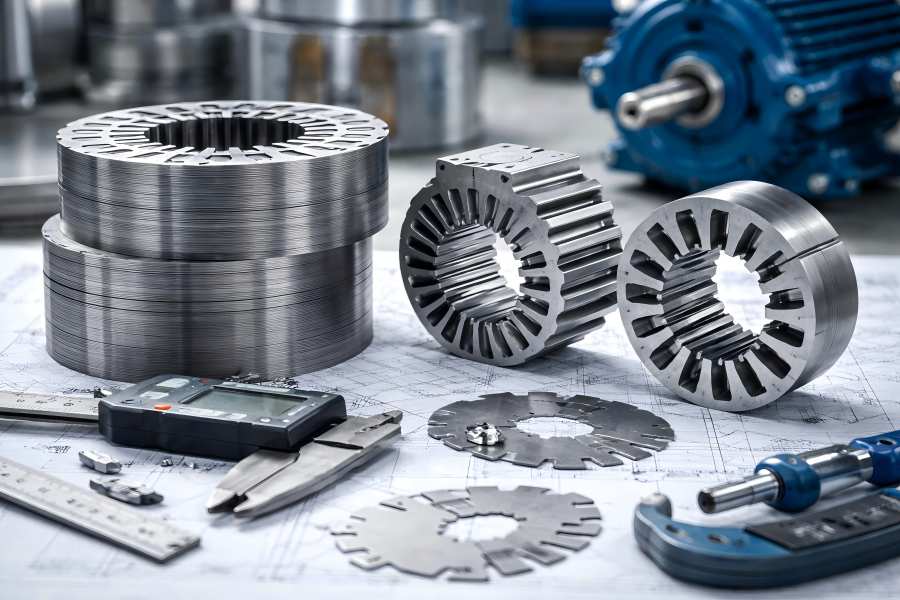
Motor laminations are integral components in the design of electric motors, particularly in minimizing energy losses and improving motor efficiency. As motors evolve in terms of power density and performance, understanding the impact of lamination thickness has become crucial.
Read Article
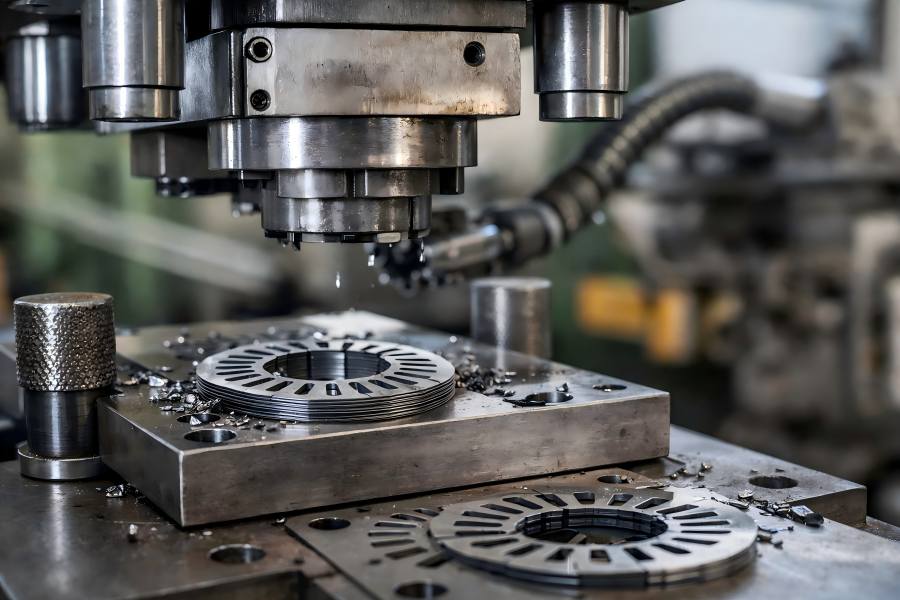
The manufacture of lamination stack assemblies is crucial in the electric motor industry. Whether for industrial motors or electric vehicles, lamination stacks significantly impact motor performance, efficiency, and reliability.
Read Article
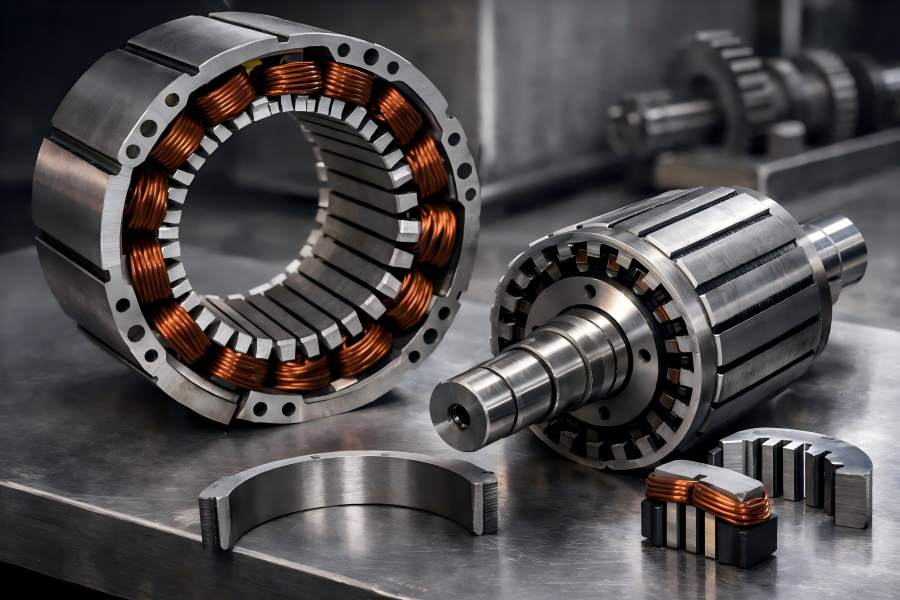
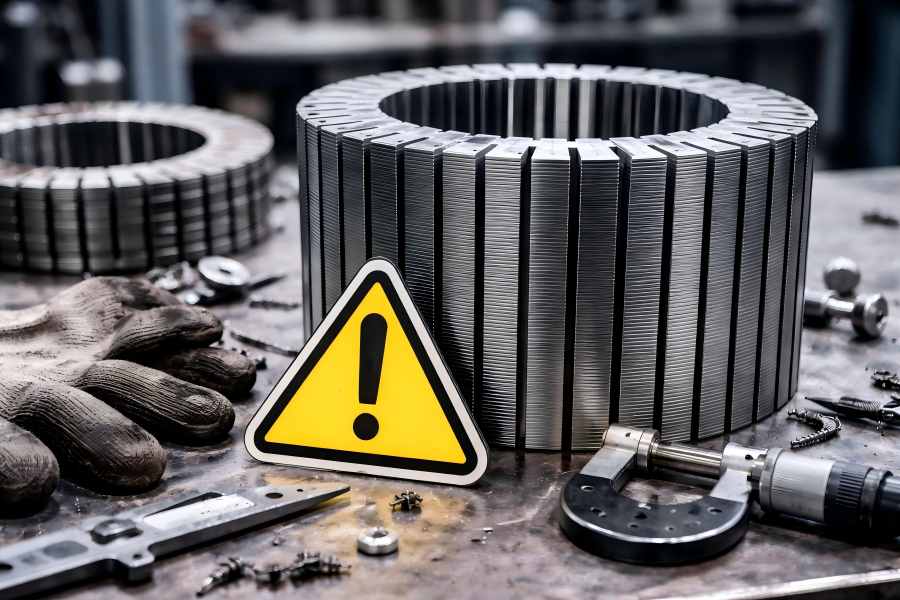
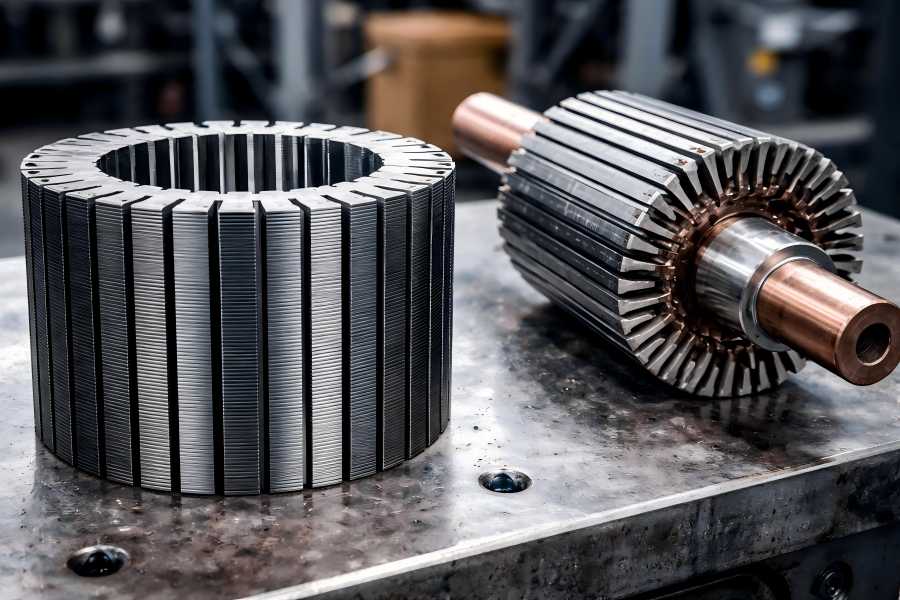
The stator and rotor lamination stacks are the two fundamental parts. While often overlooked, these parts are vital for motor efficiency and longevity. Understanding their differences and roles helps engineers and buyers make informed decisions when selecting or comparing motors.
Read Article
While failures often result from worn bearings or insulation breakdown, one critical issue is misalignment between the stator and rotor. When misaligned, the imbalance leads to performance issues, efficiency losses, and costly breakdowns.
Read Article
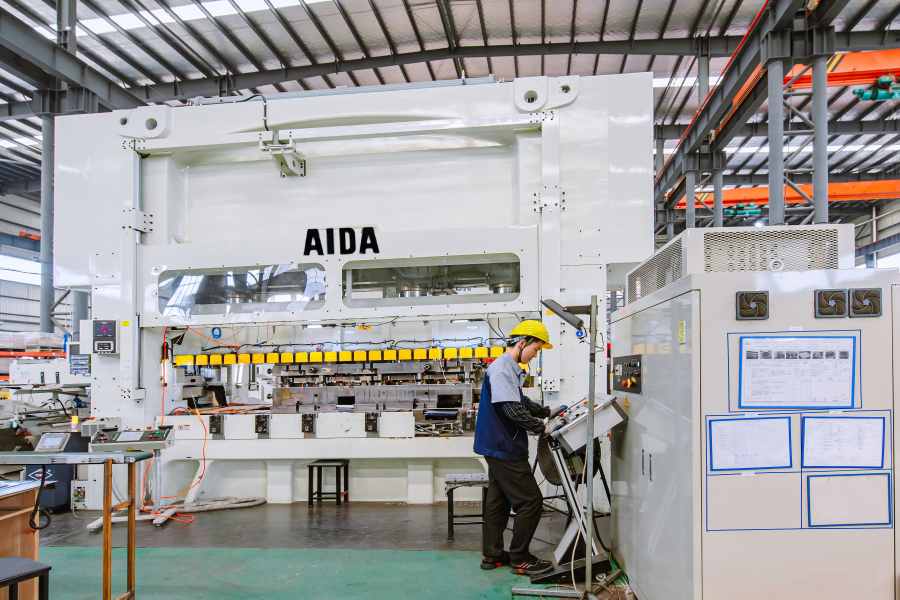
Progressive high-speed stamping is a critical manufacturing process for motor laminations, impacting part quality, throughput, and overall production cost.
Read Article
Motor lamination stamping directly affects magnetic performance, efficiency, and reliability in electric motors used across EV, industrial, appliance, and renewable energy applications.
Read Article
Electric motors and generators power modern equipment across industries, transportation, and energy systems. The motor lamination steel grade used in the core plays a critical role in efficiency, loss reduction, and long-term reliability.
Read Article