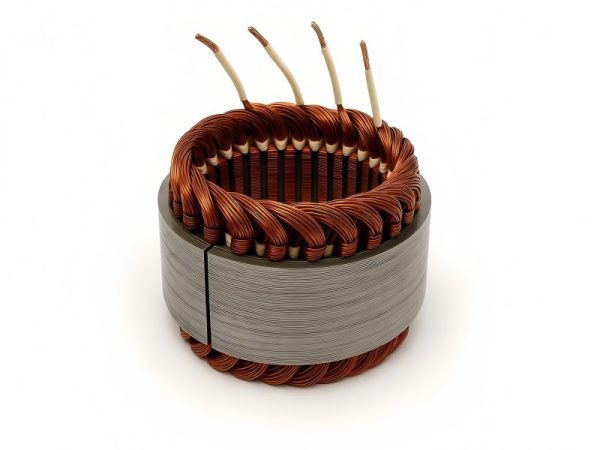
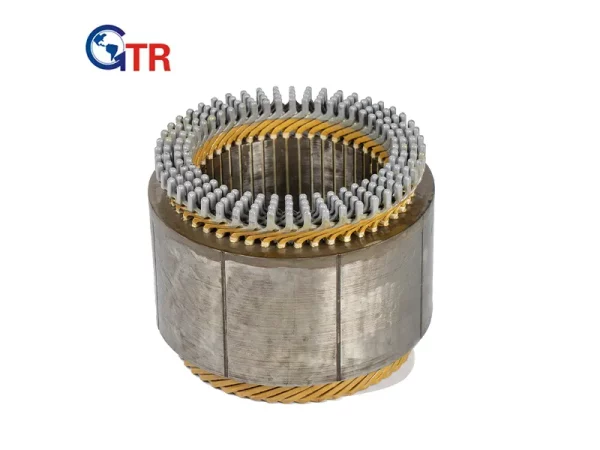
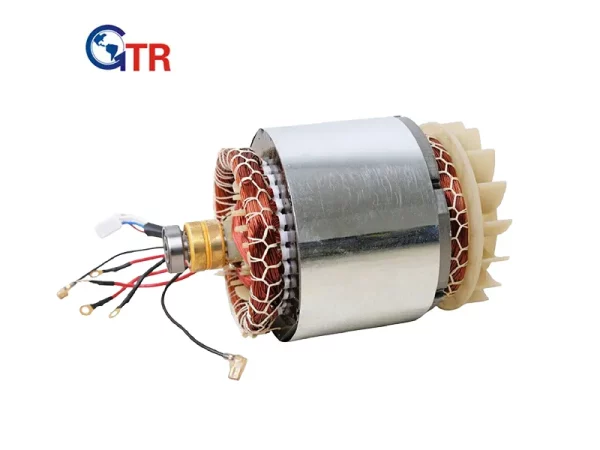
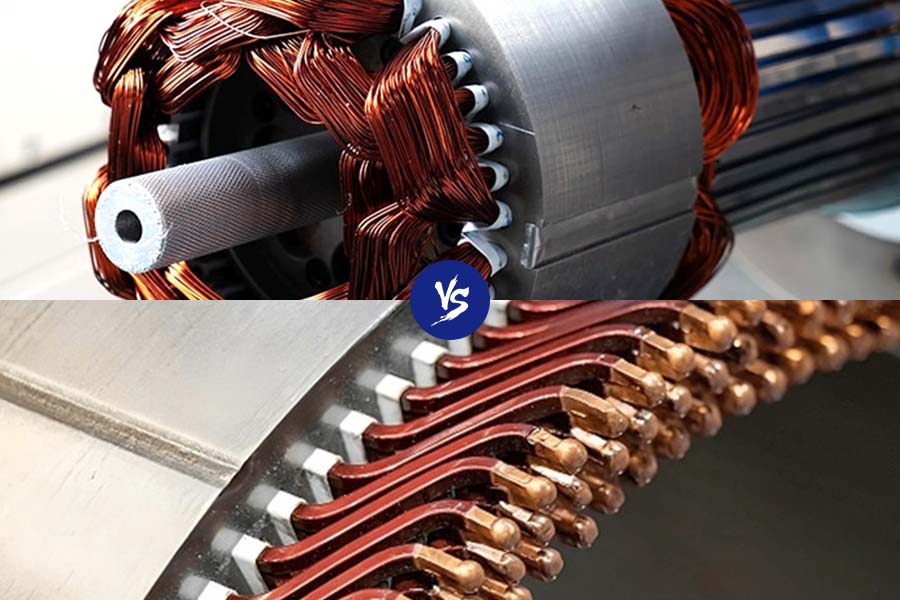
Since they transform electrical energy into mechanical power, electric motors are crucial to modern technologies. The efficiency and performance of a motor depend heavily on the material used for the stator windings. Two common options are round and flat copper wire, each offering distinct advantages.
What is Stator Winding?
Stator winding consists of wire coils around the stator in an electric motor, generating a magnetic field that makes the rotor spin and produces mechanical motion. The wire material and shape affect the motor’s efficiency, power, and lifespan.
Copper wire has been the traditional choice due to its conductivity and stability, but flat copper wire is becoming more popular, especially for high-performance and compact motors.
A Quick Comparison
To summarize the differences between round and flat copper wire for stator windings, here is a comparison table:
| Feature | Round Copper Wire | Flat Copper Wire |
| Slot Fill Rate | Lower, less efficient use of available space | Higher, more efficient packing in stator core |
| Electrical Conductivity | Excellent conductivity, standard performance | Similar conductivity, but reduced copper loss |
| Heat Dissipation | Standard heat dissipation | Superior heat dissipation due to larger surface area |
| Cost | More affordable | More expensive due to complex manufacturing process |
| Suitability for High-Power Motors | Less suitable for high-power, compact designs | Ideal for high-power, compact motors |
| Manufacturing Complexity | Simple winding process | Requires specialized winding equipment |
| Application | General-purpose motors, low-to-medium power | High-performance motors, space-constrained designs |
| Performance Efficiency | Moderate efficiency for general applications | Higher efficiency with reduced energy loss |
Round Copper Wire
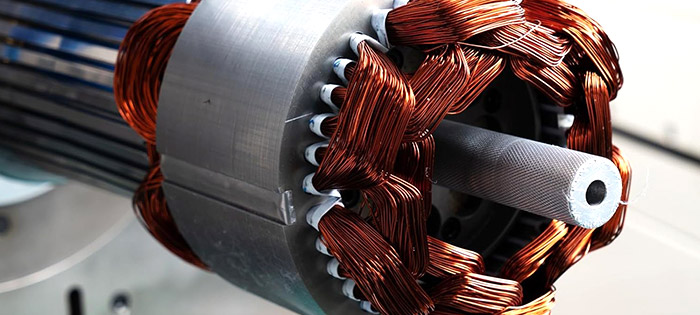
Round copper wire has long been the go-to choice for stator windings in many electric motors. Its simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and reliable performance have made it the standard for low- to medium-power motors, such as those used in home appliances, industrial equipment, and other general-purpose applications.
Advantages of Round Copper Wire:
- Good Electrical Conductivity: Round copper wire offers excellent electrical conductivity, minimizing energy losses and ensuring efficient current flow through the stator winding.
- Simplicity in Handling and Winding: The round shape of the wire makes it easier to handle and wind onto the stator core, reducing manufacturing complexity. This simplicity helps streamline the production process, lowering costs for manufacturers.
- Stability: Round copper wire provides stable and consistent performance over time, making it ideal for general motor applications that do not require cutting-edge efficiency.
- Cost-Effective: As one of the most common types of copper wire, round wire is relatively inexpensive, making it a cost-effective solution for a wide range of motor applications.
- Versatility: Suitable for low- to medium-power motors, round copper wire can be used in a variety of applications, including household fans, pumps, and small machinery.
Despite its many advantages, round copper wire does have limitations. The main drawback is its relatively low slot fill rate, meaning it occupies less space in the stator core compared to flat copper wire. This reduces the overall efficiency and performance of the motor, particularly in high-power or compact designs.
Flat Copper Wire
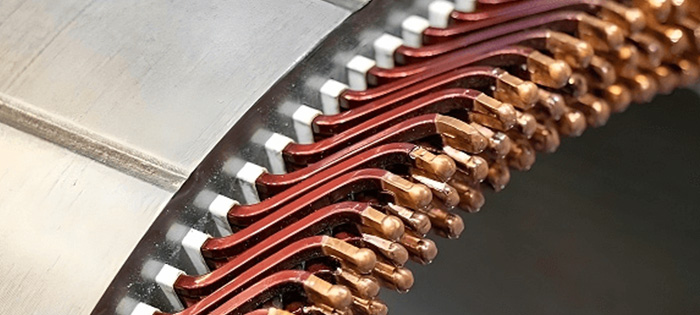
Flat copper wire, as the name suggests, features a flat cross-sectional shape, offering better space utilization within the stator core. This wire type has gained popularity in recent years due to its higher slot fill rate, improved efficiency, and superior heat dissipation properties.
It is now commonly used in motors where performance and space optimization are critical, such as electric vehicles, robotics, and high-speed machinery.
Advantages of Flat Copper Wire:
- Higher Slot Fill Rate: Flat copper wire can be wound more densely into the stator core, increasing the slot fill rate and thereby improving the motor’s winding density. This makes better use of available space and enables a motor package to have a higher power output.
- Reduced Copper Loss: With a higher slot fill rate, flat copper wire reduces copper loss, which means more of the electrical energy is effectively converted into mechanical power. The overall motor efficiency rises as a result.
- Better Heat Dissipation: With a greater surface area due to the wire’s flat design, heat dissipation during motor running is improved. This is particularly important for motors that operate under high loads or in demanding environments, where overheating can lead to damage or reduced performance.
- Better Performance for High-Power Motors: The higher efficiency and reduced losses provided by flat copper wire make it ideal for high-performance motors used in applications like electric vehicles, industrial robots, and advanced machinery.
- Compact Design: Due to its better packing efficiency, flat copper wire is often used in motors with compact designs. It allows engineers to optimize space without compromising on motor performance, which is crucial for modern devices and vehicles.
While flat copper wire offers impressive performance, it is more expensive and requires specialized winding equipment. The manufacturing process is more complex than that of round copper wire, which can make it less cost-effective for general-purpose motors.
Which Wire Is Best for Your Motor?
Choosing between round copper wire and flat copper wire depends largely on the specific needs of your motor design.
- Round Copper Wire is ideal for general-purpose motors that do not require cutting-edge performance or efficiency. It is best suited for applications where cost-effectiveness, simplicity, and reliability are the primary concerns, such as household appliances, small pumps, and low-to-medium power machinery.
- Flat Copper Wire is better suited for high-performance motors where space optimization, efficiency, and power output are critical. It excels in motors used in electric vehicles, robotics, aerospace, and high-speed machinery, where maximizing power and minimizing losses are paramount.